Types of Surgical Instruments
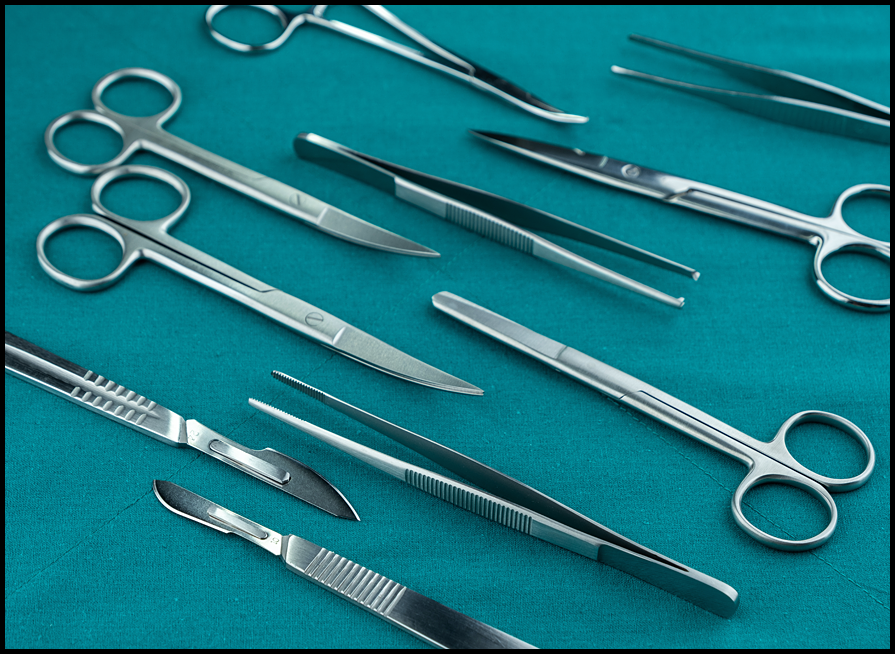
Surgical instruments are truly the unsung heroes in medical procedures. From the micro alligator forceps to the heftiest bone rasp, these tools make precision possible. In fact, surgical instrument are the bridge between a surgeon’s intent and actual outcome. I think it’s fair to say you don’t realize how critical they are until you’ve seen a procedure without them.
Anthony Products has been crafting specialized surgical tools since 1969 and has built a reputation in ENT, plastic surgery, medical instruments, instrument in surgery, oral maxillofacial, and dermatology circles. Our heritage, straight from the family garage to an international distributor, is quite something, and it adds a layer of trust when you're choosing precision instruments for critical clinical uses.
19 Common Types of Surgical Instruments
The major categories types of surgical instruments, their functions, and uses in medical procedures for precision, safety, and effective patient care.
1. Biopsy Punches
Definition/Purpose
Designed for quick and accurate removal of small cylindrical shape tissue samples for diagnostic examination.
Variants
- Standard Biopsy Punches – Seamless stainless steel razor sharp cutting edges for clean, precise specimen.
- Short Handled Biopsy Punches – Designed for hard to reach areas of the body.
Clinical Applications
- Suspicious Growths – Utilized by dermatologist to diagnosis skin abnormalities including moles, lesions, and skin cancers.
- Chronic Skin Conditions – Evaluation of chronic skin rashes for example psoriasis, eczema, and dermatitis.
- Oral Tissue Sampling – Used to identify mouth lesions including ulcers, oral cancers and other suspection abnormalities.
Shop for Biopsy Punch Instruments
2. Bone Instruments
Definition/Purpose
Designed to cut, shape, hold, crush or manipulate bone and surrounding tissues during surgical procedures.
Variants
- Curettes – Designed for scraping or scooping bone tissue with precision.
- Cartilage Bone Crushers – Used for crushing cartilage and bone into smaller fragments for grafting or reconstruction.
- Bone Rongeurs & Cutters – For trimming, cutting, and removing small bone fragments with clean, controlled action.
- Osteotomes & Bone Chisels– Sharp-edged tools ideal for sculpting, splitting, or reshaping bone.
- Bone Mallets – Used with chisels and osteotomes to deliver controlled force for bone cutting and shaping.
- Bone Rasps & Files – For smoothing and contouring bone surfaces.
Clinical Applications
- Facial Trauma – Essential for plastic and reconstructive physicans when repairing facial damage and correcting abnormalities.
- Mouth & Jaw Procedures – Used by oral and maxillofacial surgeons to treat injuries, and defects of the mouth, jaws, and face.
- Enhance Facial Appearance – Utilized in cosmetic surgery for facelifts, rhinoplasty blepharoplasty, otoplasty, and facial implants.
- ENT Procedures – Used during sinus procedures, mastoid surgery, nasal fracture repair, orbital, and facial trauma reconstruction.
- Musculoskeletal Surgery – Used in orthopedic surgery for fracture repairs, joint replacements, bone grafting, and reshaping bones.
3. Dermasurgical Instruments
Definition/Purpose
Used for precise manipulation of skin and soft tissue in dermatologic procedures.
Variants
- Comedone Extractors – Designed for extracting blackheads and whiteheads.
- Skin Hooks – Fine hooks for gentle retraction of skin during surgery.
- Dermasurgical Scissors (Iris, Tenotomy, etc.) – For delicate cutting of skin or soft tissue.
- Dermasurgical Forceps – Fine-tipped or toothed instruments used for grasping and holding tissue.
- Scalpels & Blades – For precise incisions and excisions of skin lesions or tumors.
- Dermasurgical Needle Holders – Designed for precise control and suture placement.
- Biopsy Punches – Seamless stainless steel razor sharp cutting edges for clean, precise specimen.
Clinical Applications
- Excision of Lesions – Removal of benign or malignant skin growths such as cysts, moles, or tumors.
- Skin Biopsies – Obtaining tissue samples for accurate pathological diagnosis.
- Acne & Comedone Treatment – Safe extraction of blackheads, whiteheads, and cysts.
Shop for Dermasurgical Instruments
4. ENT (Ear, Nose & Throat) Instruments

Definition/Purpose
Specialized surgical tools designed for the diagnosis, treatment, and surgical management of conditions affecting the ear, nose, and throat.
Instrument Variants
- Ear Specula – Used to widen the ear canal for clear visualization of the middle ear and tympanic membrane.
- Ear Curettes & Loops – Designs for manual safe removeal cerumen extraction, also known as earwax.
- Foreign Body Removal Instruments – Utilized to extract objects stuck inside the ear canal (beads, insects, food particles, etc.)
- Suction Tubes – Precise suction tips for removing debris or fluids from the ear and nasal canals.
- Myringotomy Blades – Specialized blades for incision of the tympanic membrane in middle ear procedures.
- Tuning Forks – Quickly evaluate a patient’s hearing ability without the need for electronic equipment.
Clinical Applications
- Ear Examination & Cleaning – Visualization of ear canal, removal of cerumen/foreign bodies, and hearing assessment.
- Myringotomy/Tympanostomy – Incision of tympanic membrane, insertion of tubes, aspiration of fluid, middle.
- Tympanoplasty – Repair of tympanic membrane and middle ear structures.
- Nasal Exams & Procedures – Visualization of nasal passages, dressing placement/removal, correction and reshaping nasal structures.
- Tonsillectomy/Adenoidectomy – Removal of tonsils and adenoids, visualization of larynx and vocal cords, removal of foreign bodies.
5. Elevators

Definition/Purpose
Used to lift, separate, and elevate soft tissue or bone, especially the periosteum, ENT, maxillofacial and plastic surgeries.
Instrument Variants
- Periosteal Elevators – Used to separate periosteum (the thin tissue covering bone) from the bone surface.
- Freer Elevators – Multi-purpose elevators commonly used in ENT, plastic, and orthopedic surgeries for soft tissue dissection.
- Cottle Elevators – Primarily used in rhinoplasty and nasal surgeries for cartilage and soft tissue elevation.
Clinical Applications
- Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery – Tooth extraction, flap reflection, and bone exposure.
- ENT Surgery – Nasal reconstruction, sinus surgery, and tympanoplasty.
- Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery – Delicate tissue lifting for facial procedures and grafts.
- Orthopedic Surgery – Elevating periosteum, handling bone grafts, or separating soft tissue layers.
6. Forceps

Definition/Purpose
Designed for grasping, holding, manipulating, or extracting tissues and objects during medical procedures.
Variants
- Tissue Forceps – Grip and stabilize tissue during suturing or dissection.
- Dressing Forceps – Used for handling dressings, sponges, or non-living materials.
- Hemostatic Forceps (Clamps) – Controls bleeding by clamping blood vessels.
- Ears Forceps (Alligators) – Designed for use in the narrow and delicate passages of the ear canal.
- Nasal Forceps – Used for nasal packing, foreign body removal and excising nasal polyps.
- Throat Forceps – Features long shafts to reach deep into the pharynx and larynx without obstructing visibility.
- Ophthalmology Forceps – Extremely fine tipped instruments designed specifically for eye surgery and delicate ocular procedures.
- Plastic Surgery Forceps – Emphasizes precision, control, and minimal tissue trauma during plastic and reconstructive procedures.
Clinical Applications
- General Surgery – Holding and stabilizing tissues, aiding suturing, and controlling bleeding.
- ENT (Ear, Nose, Throat) – Removing wax, foreign bodies, or polyps; handling dressings; and assisting in ear, nasal, and throat surgeries.
- Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery – aligning delicate skin edges, handling grafts and flaps, and assisting in fine cosmetic closures.
- Ophthalmology – Handling delicate eye tissues, removing foreign bodies, and assisting in cataract or retinal surgeries.
- Bleeding Control – applied in virtually all surgical fields for clamping blood vessels to stop bleeding.
- Emergency Medicine – removing foreign bodies and assisting with airway or wound management.
7. Fiber‑Optic Surgical Instruments

Definition/Purpose
Specialized tools that integrate fiber-optic technology to deliver bright, focused light exactly where the surgeon is working.
Instrument Variants
- Fiber-Optic Retractors – Illuminate the surgical site while retracting tissue during plastic surgery procedures.
- Fiber-Optic Suctions – Provide both illumination and suction for clearing fluids or blood while maintaining visibility.
- Fiber-Optic Nasal Specula – Assists in accessing and illuminating the sinuses.
- Fiber-optic Smoke Evacuation – Clears smoke plume while maintaining a well-lit, unobstructed surgical field.
Clinical Applications
- Breast Procedures – Provides deep, illumination during breast augmentation, reconstruction and mastectomies.
- Facelift & Plastic Surgery – Retracts facial skin and subcutaneous tissue while illuminating the operative field.
Shop for Fiber-optic Surgical Instruments
8. Implant Instruments

Definition/Purpose
Tools used in the placement and positioning of surgical implants.
Variants
- Insertion forceps
- Marking tools
- Guide devices
Clinical Applications
- Breast Augmentation
- Facial and Nasal Implant placement
- Reconstructive plastic surgery
Shop for Implant Surgical Instruments
9. Measuring Instruments

Definition/Purpose
Tools used to obtain precise measurements during medical or surgical procedures. Their purpose is to ensure accuracy, symmetry, and proper sizing of tissues, bones, implants, or incisions
Instrument Variants
- Calipers – Precision instruments that measure point-to-point precision distances to fractions of a millimeter.
- Rulers – Used for general measurements to the nearest millimeter on flat or curved surfaces.
- Goniometer – Functions like a protractor designed to measure a range of motion in small joints.
- Projectometer – Used to obtain preoperative baseline measurement of tip projection during rhinoplasty procedures.
- Breast Measuring Tools – Used by surgeons to take precise breast measurements for symmetry and proportion.
- Brow Lift Drill Guide – used in brow lift procedures to ensure precise placement of screws or anchors in the skull or frontal bone
Clinical Applications
- Ophthalmology – Obtain millimeter-level precision needed in delicate eye examinations and surgeries.
- Rhinoplasty – Used for accurate evaluation of dorsal humps, tip projection, or bridge width.
- Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery – Measure facial tissue, grafts, and implants for accurate, symmetrical results.
- Mammoplasty – Used to measure and guide breast size, shape, and symmetry before, during, and after surgery for accurate, balanced results.
Shop for Measuring Surgical Instruments
10. Nasal Instruments
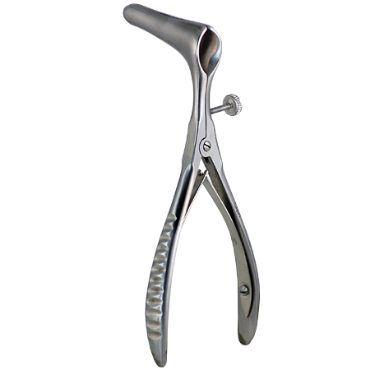
Definition/Purpose
Instruments designed for nasal procedures involving trimming, exposure, or suction.
Variants
- Hooks, knives, punches
- Specula, retractors
- Frontal Seekers, trocars
Clinical Applications
- Rhinoplasty
- Septoplasty
- Sinus surgeries
Shop for Nasal Surgical Instruments
11. Needle Holders
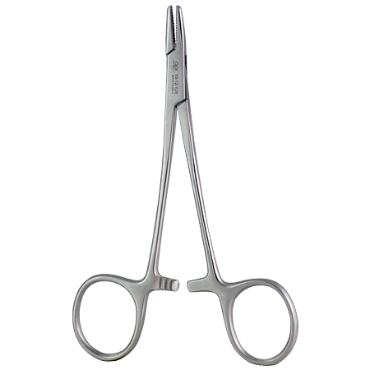
Purpose
Allows precise control when suturing tissue by securely gripping the needle with a locking mechanism and specially designed tips that prevent slipping or damage
Instrument Variants
- Mayo-Hegar Needle Holder – The most common type; robust, with a simple cross-hatch jaw for general suturing.
- Crile-Wood Needle Holder – Finer, with a more delicate grip for precise work.
- Castroviejo Needle Holder – Extremely fine tips, often spring-loaded; used in microsurgery, ophthalmic, or vascular procedures.
- Mathieu Needle Holder – Spring-loaded handles with a ratchet-less design for quick suturing in confined spaces.
Tungsten Carbide Inserts
Some needle holders feature tungsten carbide inserts bonded to the inner surfaces of their jaws. These inserts provide a much harder and more durable gripping surface compared to standard stainless steel. Tungsten carbide needle holders are easily identified by their gold handles, which indicate the presence of tungsten carbide inserts.
The benefits of these tungsten carbide inserts include:
- Superior Grip: The TC inserts prevent the needle from slipping during suturing, allowing for more precise control.
- Increased Durability: Tungsten carbide is extremely hard and wear-resistant, so the jaws maintain their texture and effectiveness far longer.
- Less Maintenance: Because they resist wear and corrosion, TC needle holders require less frequent replacement.
12. Ophthalmology Instruments
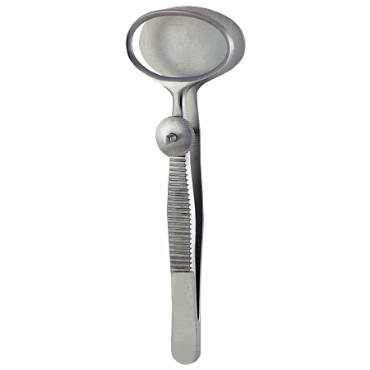
Definition/Purpose
Used during eye surgeries to perform precise procedures on delicate eye structures. They are designed for accuracy, minimal tissue damage, and safety, since the eye is extremely sensitive and small.
Variants
- Scissors and Forceps – For precise cutting and tissue manipulation.
- Needle Holders – Used for suturing delicate eye tissues.
- Speculum – Holds eyelids open during surgery.
- Probes – Examine, dilate, and clear the lacrimal (tear) drainage system.
- Eye Shields – Safety devices that protect a patient’s eyes from accidental injury during laser surgical procedures.
Clinical Applications
- Blepharoplasty Surgery: Manipulation, removing and reshaping excess eyelid tissue.
- Microsurgery in ENT-Related Areas: Procedures on the lacrimal sac, eyelids, or conjunctival region.
- Skin Grafts or Flap Procedures: Precise handling of tiny grafts or flaps near the eyelids or orbital area.
Shop for Ophthalmology Instruments
13. Plastic Surgery Instruments

Definition/Purpose
High-precision instruments tailored for aesthetic and reconstructive surgeries.
Variants
- Areola markers
- Dissector tools
- Retractors
- Endoscopic forehead devices
Clinical Applications
- Breast augmentation and lifts
- Facial cosmetic surgeries
- Endoscopic brow lifts
Shop for Plastic Surgery Instruments
14. Retractors

Definition/Purpose
Hold back tissues or incisions to maintain visibility and access during surgery.
Variants
- Deaver, Army-Navy, Richardson
- Self-retaining: Weitlaner, Beckman
- Throat, nasal, ophthalmic, plastic surgery models
Clinical Applications
- ENT, orthopedic, general, and plastic surgery
- Tissue separation and cavity access
15. Scalpel Blades & Handles

Definition/Purpose
Used to make precise incisions in tissue.
Variants
- Disposable or reusable handles
- Blade types: #10, #11, #15
- Specialty blades: Myringotomy
Clinical Applications
- General incisions
- ENT-specific blade sets
Shop for Surgical Blades & Handles
16. Scissors

Definition/Purpose
Used in medical procedures to cut tissue, sutures, or other materials in a controlled and precise manner. They are designed for accuracy, safety, and ease of use in surgical settings
Variants
- Operating Scissors – The most common type of scissors in an operating room, designed for versatility rather than specialized tasks.
- Metzenbaum Scissors – Long, thin scissors for designed for delicate tissue dissection.
- Mayo Scissors – Heavy-duty surgical scissors for cutting tissue or sutures that require more strength.
- Iris Scissors – Small, precise scissors often used where accuracy is essential including eye surgery.
- Bellucci Ear Scissors – designed for precision cutting in small, delicate areas of the ear.
Clinical Applications
- Cutting Tissue – Straight or curved scissors for general tissue dissection.
- Fine or Delicate Work – Micro scissors for precise procedures like ophthalmology or plastic surgery.
- Suture Removal – Small scissors with a blunt tip to safely cut stitches.
- Bandage Scissors – Safely cuts bandages, dressings, or clothing near a patient’s skin without causing injury.
- Septal Scissors – A heavy duty scissor designed for cutting tough septal cartilage and bony tissue.
Tip/Blade Options
- Sharp Tips – Precise, allow piercing or fine cutting. Used where accuracy is critical.
- Blunt Tips – Safer, less likely to puncture tissue. Used for general tissue dissection.
- Straight Tips – Precise, controlled cuts on flat or superficial tissue.
- Curved Tips – Follows contours, better for deep or delicate dissection.
- Tungsten Carbide – Durable, high-precision scissors with tungsten carbide cutting edges that stay sharp longer, commonly used in microsurgery, plastic surgery, and cardiovascular procedures.
- Super-Cut Blades – Razor-sharp upper blade for effortless tissue cutting, with a micro-fine serrated lower blade to securely hold tissue.
17. Skin Hooks

Definition/Purpose
Designed to gently grasp, lift, and retract skin or soft tissue during minor and dermatologic surgeries.
Variants
- Cook Skin Hooks – Provides gentle retraction of delicate tissue
- Cottle Hook Retractors – Offers broad, stable retraction in facial and nasal procedures
- Frazier Skin Hooks – Delicate dermatologic procedures requiring precision
- Freer Skin Hooks – Often used for delicate tissues in procedures like rhinoplasty
Hook Types
- Single Prong – Features one sharp hook at the tip and is ideal for delicate or thin skin and soft tissue. Causes minimal trauma making them ideal for plastic surgery and minor dermatologic procedures.
- Double Prong – Designed with two hooks at the tip to provide a firmer grip on thicker or tougher tissue. Offering more traction than single-prong hooks, they are commonly used in general surgery for secure retraction.
- Sharp vs. Blunt Tip Hooks – Sharp tips allow precise, firm grasping of skin edges, while blunt tips reduce the risk of puncturing fragile tissue or areas near underlying structures.
18. Suction Tubes

Definition/Purpose
Used to remove fluids, blood, mucus, or debris from the surgical or examination field during ear, nose, and throat (ENT) procedures.
Variants
- Frazier Suction Tubes – Allows precise suction in small or delicate areas; suction controlled via the thumb hole.
- Baron Suction Tubes – Provides versatility for different ear surgeries, maintaining precision while preventing trauma.
- Yankauer Suction Tubes – Designed for bulk suctioning in oral and throat procedures without damaging tissue; ideal for removing mucus, saliva, or blood from the oropharynx
Clinical Applications
- Ear Procedures – Removing wax, infection drainage, or fluid from the ear canal or middle ear (e.g., during myringotomy).
- Nasal Surgeries – Clearing blood and mucus during sinus or septal operations.
- Throat Procedures – Suctioning saliva, blood, or secretions during tonsillectomy or other oropharyngeal surgeries.
19. Suture Removal Instruments
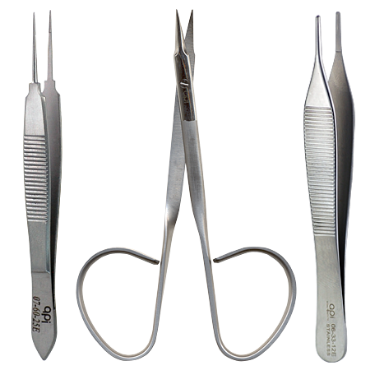
Purpose
Remove sutures post‑procedure, with minimal tissue trauma.
Applications
Outpatient follow‑ups; dermatologic, plastic, or general surgical settings.
Clinical Applications
- ENT, dermatology, general surgery
- Maintaining clear surgical visibility
Shop for Suture Removal Instruments
Specialty Highlights
Tungsten Carbide Instruments
Needle holders and scissors often come in with tungsten carbide tips for durability, sharper grips, longer edge retention. Surgeons appreciate the precision and longevity.
Disposable Myringotomy Blades
ENT professionals may choose flat, round, or micro‑edge blades depending on patient need. Anthony Products offers sets specialized for ENT practice.
Quality & Compliance
High-quality surgical instruments are manufactured to meet strict clinical standards. At Anthony Products, we prioritize precision and compliance, providing instruments that deliver consistent reliability in every procedure.
Why Choose Anthony Products?
Founded in 1969, Anthony Products brings over half a century of expertise to the ENT, plastic surgery, dermatology, and oral maxillofacial fields. Today, we offer a comprehensive catalog of more than 100,000 trusted surgical instruments, serving tens of thousands of professionals worldwide.
We provide personalized service, every online order is manually reviewed to catch errors and ensure you receive exactly what you need, with one-on-one support you won’t find at large, impersonal retailers.
How to Order / Resources
If you’re setting up a new practice or replenishing your instrument inventory, Anthony Products’ website is straightforward. Browse by category (e.g. Dermasurgical, ENT, Fiber‑Optic Products), then reach out to our customer service for custom needs or questions. We provide literature, product manuals, FAQs, and international shipping. You can contact us page.
Final Thought
Surgical success depends on tools that align with the surgeon’s intent. That’s why it’s important to understand commonly used surgical instruments—not just their names, but their functions, differences, and proper applications.
Since 1969, Anthony Products has built a trusted legacy of providing high-precision, compliant surgical instruments. From biopsy punches and retractors to forceps and delicate tungsten-carbide needle holders, we offer everything you need for dependable performance.
Ultimately, surgical precision depends on the instruments used—and selecting the right tools for each procedure isn’t just important; it’s essential.




